Introduction
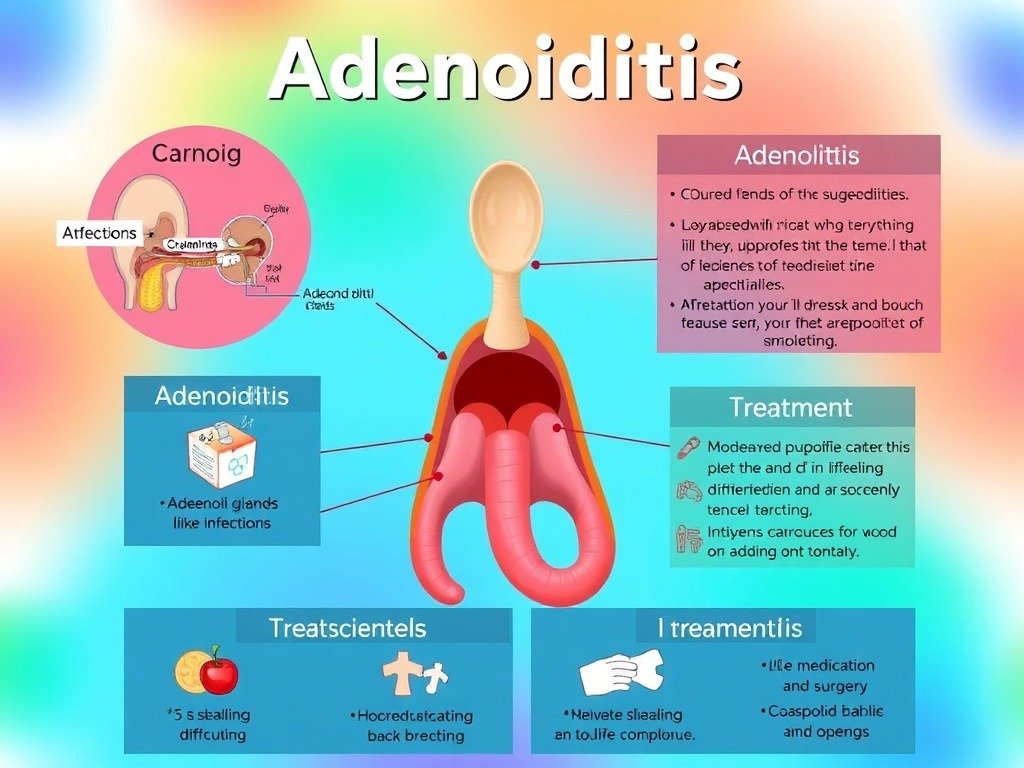
Adenoidid, commonly referred to as adenoid inflammation, is a medical condition that primarily affects the adenoids—small patches of tissue located in the upper part of the throat, behind the nose. These glands play a critical role in a child’s immune system by trapping harmful bacteria and viruses. However, when they become swollen or infected, they can cause a variety of health issues that affect breathing, swallowing, and overall comfort. Adenoidid is more common in children than adults, as adenoids tend to shrink naturally with age. Still, understanding the root causes and best treatment methods is essential for both parents and adults dealing with lingering symptoms.
What Are Adenoids and Their Role?
Adenoids are part of the lymphatic system and function as the first line of defense against pathogens entering through the nose and mouth. They work closely with the tonsils to filter out bacteria and viruses, supporting the immune system’s ability to fight infections. In children, these glands are highly active because their immune systems are still developing. Over time, however, their role diminishes, and they naturally reduce in size, which is why adenoid problems are rare in adults.
Causes of Adenoidid
Adenoidid usually develops due to infections caused by bacteria or viruses, though allergies and environmental irritants can also trigger inflammation. Factors such as recurrent respiratory infections, chronic sinusitis, and prolonged exposure to polluted air increase the risk of adenoid swelling. Children attending school or daycare are more susceptible because of constant exposure to germs. In rare cases, genetic predisposition may make certain individuals more likely to develop recurring adenoid issues.
Common Symptoms of Adenoidid
The symptoms of adenoidid vary depending on the severity of the inflammation. While mild cases might only cause minor discomfort, severe infections can significantly impact daily life.
Common symptoms include:
- Difficulty breathing through the nose
- Persistent nasal congestion
- Snoring or noisy breathing during sleep
- Recurrent ear infections or fluid buildup in the ears
- Sore throat or difficulty swallowing
These symptoms can disrupt sleep patterns and affect a child’s ability to concentrate during the day, making early detection and treatment important.
How Adenoidid Affects Breathing and Sleep
One of the most noticeable effects of adenoidid is on breathing. Swollen adenoids can block the airway, forcing a child to breathe through the mouth. This can lead to dry mouth, bad breath, and even facial development issues over time. Sleep problems such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) are also common. Children may wake up frequently at night, gasp for air, or display restless sleeping patterns, which can result in daytime fatigue and irritability.
Diagnosis: How Doctors Identify Adenoidid
Diagnosis typically begins with a physical examination, where a doctor checks the back of the throat using a small mirror or flexible scope. In some cases, imaging tests like X-rays may be used to assess the size of the adenoids. Doctors may also recommend a hearing test if recurrent ear infections are present. Proper diagnosis ensures that the treatment plan targets the root cause of the problem, rather than just relieving symptoms temporarily.
Medical Treatment Options for Adenoidid
Treatment depends on the severity of the condition. For mild cases, doctors may recommend home remedies and over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms. Antibiotics are prescribed if a bacterial infection is confirmed. Nasal sprays containing corticosteroids can help reduce swelling and improve airflow. In chronic or severe cases where adenoids remain enlarged, surgical removal (adenoidectomy) may be necessary.
Surgical Intervention: Adenoidectomy
Adenoidectomy is a short surgical procedure where the adenoids are removed through the mouth without any external cuts. It is usually performed under general anesthesia and takes less than 30 minutes. Recovery is generally quick, with most children resuming normal activities within a week. This surgery is often recommended when adenoidid leads to frequent ear infections, breathing problems, or persistent sinus issues.
Home Remedies and Care Tips
While medical intervention is sometimes unavoidable, certain home care methods can help manage mild symptoms and prevent recurrence:
- Use a humidifier to keep nasal passages moist
- Encourage proper hydration throughout the day
- Maintain a clean, dust-free environment
- Avoid exposure to cigarette smoke and strong allergens
- Support a balanced diet to strengthen the immune system
These preventive measures reduce the risk of repeated infections and support overall respiratory health.
Adenoidid in Children vs. Adults
Although adenoidid is far more common in children, adults can also experience it, particularly if they have chronic allergies or respiratory infections. The symptoms in adults are generally similar but may be mistaken for sinusitis or allergies, leading to delayed treatment. Adults with persistent nasal blockage, recurrent sore throats, or sleep disturbances should consult a specialist to rule out adenoid problems.
Complications If Left Untreated
Ignoring adenoidid can result in several complications, including chronic ear infections, hearing loss, speech development delays, and facial structure changes in children. Persistent breathing difficulties may also cause behavioral issues due to lack of proper sleep. In severe cases, untreated adenoidid can lead to long-term respiratory problems, making timely treatment essential.
Prevention and Long-Term Management
Prevention starts with maintaining strong immunity and good hygiene. Teaching children to wash hands regularly, covering their mouths when coughing, and avoiding close contact with sick individuals can significantly lower infection risks. For those prone to adenoid problems, regular medical checkups are important for early detection and intervention.
Table: Comparing Mild vs. Severe Adenoidid Symptoms
| Aspect | Mild Adenoidid | Severe Adenoidid |
| Nasal Congestion | Occasional, manageable | Persistent, worsens over time |
| Breathing | Slight difficulty | Major blockage, mouth breathing |
| Sleep Quality | Minimal disruption | Frequent waking, sleep apnea |
| Ear Health | Rare infections | Chronic ear infections |
| Need for Surgery | Unlikely | Highly likely |
When to Seek Medical Help
Parents should seek immediate medical attention if their child exhibits severe breathing problems, high fever, or prolonged symptoms that do not improve with home treatment. In adults, any long-term nasal blockage or unexplained sleep disturbances should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out serious conditions.
Living Comfortably After Treatment
After treatment—whether through medication or surgery—most individuals experience a significant improvement in breathing, sleep quality, and overall health. Post-treatment care, such as maintaining a clean environment and following the doctor’s advice, is essential to prevent recurrence. With the right approach, recovery from adenoidid can be smooth and long-lasting.
Conclusion
Adenoidid, while common in children, is a condition that can cause considerable discomfort and health issues if left untreated. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and available treatments is key to ensuring proper care and recovery. Early diagnosis, lifestyle adjustments, and—when necessary—surgical intervention can help restore breathing, improve sleep, and prevent complications, allowing patients to lead a healthier and more comfortable life.
FAQs
1. Can adenoidid go away without treatment?
Mild cases may resolve naturally, especially in older children as adenoids shrink, but medical monitoring is recommended.
2. Is adenoid removal safe for children?
Yes, adenoidectomy is generally safe and performed frequently with minimal risks when done by experienced surgeons.
3. Can allergies cause adenoidid?
Yes, chronic allergies can trigger or worsen adenoid swelling, leading to symptoms similar to infections.